In This Topic
Step 1: Look for model relationships and assess the strength
Look for model relationships between pairs of variables. Determine which model relationship best fits your data and assess the strength of the relationship. If a model fits well, you can use the regression equation for that model to describe your data.
Tip
To see how well a particular model fits your data, add a fitted regression line. Double-click the graph. With the graph in editing mode, right-click the graph, then choose . You can hold the pointer over the fitted regression line to see the regression equation.
Type of relationship
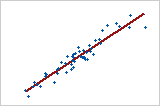
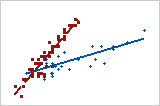
Linear: positive
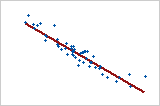
Linear: negative
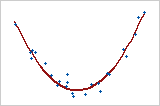
Curved: quadratic
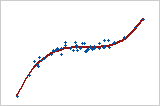
Curved: cubic
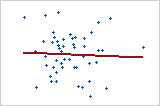
No relationship
If your data seem to fit a model, you can explore the relationship using a regression analysis.
Strength of relationship
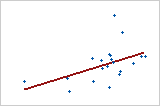
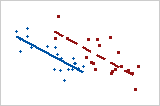
Weaker relationship
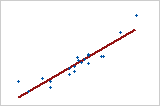
Stronger relationship
To quantify the strength of a linear (straight) relationship, use a correlation analysis.
Step 3: Look for other patterns
Outliers may indicate unusual conditions in your data. Time-based trends may indicate changing data conditions.
Outliers
Outliers, which are data values that are far away from other data values, can strongly affect your results.
On a scatterplot, isolated points identify outliers.

Try to identify the cause of any outliers. Correct any data entry or measurement errors. Consider removing data values that are associated with abnormal, one-time events (special causes). Then, repeat the analysis.
Time-based trends
If the X variable contains a sequence of time or date values recorded in order, look for time-based trends. To add connect a line to your scatterplot, double-click the graph. With the scatterplot in editing mode, right-click the graph, then choose and select Connect Line.
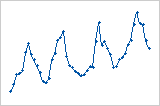
Cycling trend
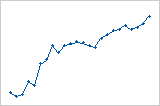
Increasing trend
Note
If you collected data in equally-spaced time intervals, you can use a time series plot.