Minitab calculates an accept or reject decision based on your measurements from sampled items and the criteria (sample size and critical distance) of your variables acceptance sampling plan.
First Minitab calculates the mean and standard deviation from your data (if you have not specified a historical standard deviation):
- Mean
-

- Standard deviation
-

- Acceptance criteria for specification limits
-
- Maximum Standard Deviation (MSD)
- If you have 2 specification limits and the standard deviation is unknown, then the MSD plays a role in accepting or rejecting the lot. For the calculation of MSD, go to Methods and formulas for Variables Acceptance Sampling (Create/Compare).
Note
Minitab uses σ instead of s in the Z calculations when you provide a historical standard deviation.
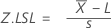
- Single specification limit
- The corresponding Z-value is calculated. If lower specification only, accept the lot if Z.LSL ≥ k; otherwise reject the lot. If upper specification only, accept the lot if Z.USL ≥ k; otherwise reject the lot.
- Double specification limits and known standard deviation
- The Z-values for each specification are calculated. Accept the lot if Z.LSL ≥ k and Z.USL ≥ k; otherwise reject the lot.
- Double specification limits and unknown standard deviation
- The Z-values for each specification and the MSD are calculated. Accept the lot if s ≤ MSD, Z.LSL ≥ k and Z.USL ≥ k; otherwise reject the lot.
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Xi | measurement data |
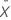 | mean |
| s | estimated standard deviation |
| σ | known standard deviation |
| n | sample size |
| k | critical distance |
| L | lower specification limit |
| U | upper specification limit |

