In This Topic
Histogram
A histogram divides sample values into many intervals and represents the frequency of data values in each interval with a bar.
Interpretation
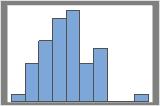
50 resamples
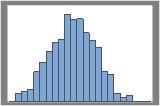
1000 resamples
The distribution is usually easier to determine with more resamples. For example, in these data, the distribution is ambiguous for 50 resamples. With 1000 resamples, the shape looks approximately normal.
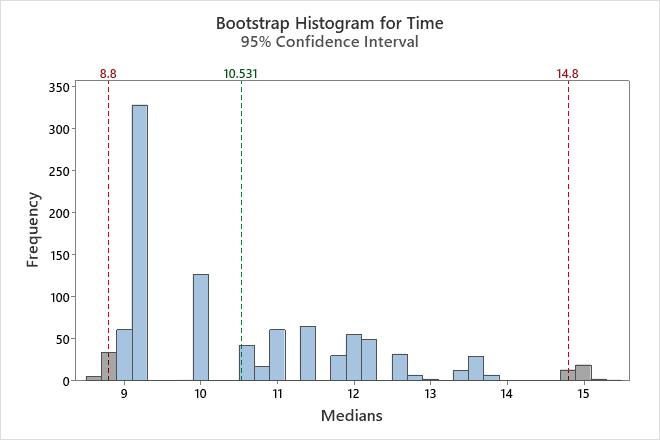
In this histogram, the bootstrap distribution does not appear to be normal. The original sample has only 16 data points. To get a reliable confidence interval, you should collect a larger sample and perform the analysis again.
Individual value plot
An individual value plot displays the individual values in the sample. Each circle represents one observation. An individual value plot is especially useful when you have relatively few observations and when you also need to assess the effect of each observation.
Note
Minitab displays an individual value plot only when you take only one resample. Minitab displays both the original data and the resample data.
Interpretation
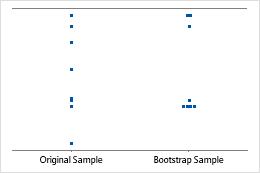
Sample size of 8
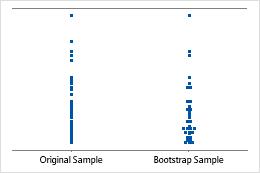
Sample size of 50
Bar chart
The bar chart shows the proportion of occurrences for each category.
Note
Minitab displays a bar chart when you take only one resample. Minitab displays both the original data and the resample data.
Interpretation
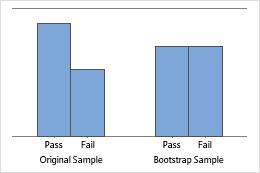
Sample size of 8
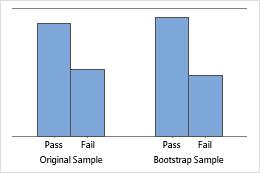
Sample size of 50
Number of Resamples
The number of resamples is the number of times Minitab takes a random sample with replacement from your original data set. Usually, a large number of resamples works best. The sample size for each resample is equal to the sample size of the original data set. The number of resamples equals the number of observations on the histogram.
Average
The average is the sum of the chosen statistics in the bootstrapping sample divided by the number of resamples.
Interpretation
Minitab displays two difference values of the chosen statistic, the value of the observed sample and the value of the bootstrap distribution (Average). Both these values are an estimate of the population parameter and will usually be similar. If there is a large difference between these two values, you should increase the sample size of your original sample.
Because the average is based on sample data and not on the entire population, it is unlikely that the average equals the population parameter. To better estimate the population parameter, use the confidence interval.
StDev (bootstrap sample)
The standard deviation of the bootstrap samples (also known as the bootstrap standard error) is an estimate of the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the chosen statistic.
Interpretation
Use the standard deviation to determine how spread out the chosen statistics from the bootstrap sample are from the overall mean. A higher standard deviation value indicates a greater spread.
Use the standard deviation of the bootstrap samples to determine how precisely the bootstrap statistic estimates the population parameter. A smaller value indicates a more precise estimate of the population parameter. A larger sample size results in a smaller bootstrap standard error and a more precise estimate of the population parameter.
Confidence interval (CI) and bounds
Confidence intervals are based on the sampling distribution of a statistic. If a statistic has no bias as an estimator of a parameter, its sampling distribution is centered at the true value of the parameter. A bootstrapping distribution approximates the sampling distribution of the statistic. Therefore, the middle 95% of values from the bootstrapping distribution provide a 95% confidence interval for the parameter. The confidence interval helps you assess the practical significance of your estimate for the population parameter. Use your specialized knowledge to determine whether the confidence interval includes values that have practical significance for your situation.
Note
Minitab does not calculate the confidence interval when the number of resamples is too small to obtain an accurate confidence interval.
Observed Sample
| Variable | N | Mean | StDev | Variance | Sum | Minimum | Median | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 16 | 11.331 | 3.115 | 9.702 | 181.300 | 7.700 | 10.050 | 16.000 |
Bootstrap Samples for Mean
| Number of Resamples | Mean | StDev | 95% CI for μ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 11.3095 | 0.7625 | (9.8562, 12.8562) |
In these results, the estimate for the population mean is approximately 11.3. You can be 95% confident that the population mean is between approximately 9.9 and 12.9.
