In This Topic
Step 1: Determine whether the proportion of defective items is in control
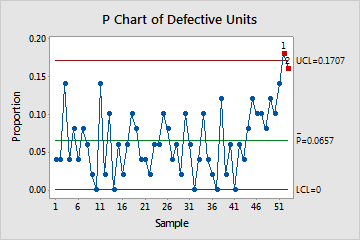
The P chart plots the proportion of defective items (also called nonconforming units) for each subgroup. The center line is the average proportion of defectives. The control limits, which are set at a distance of 3 standard deviations above and below the center line, show the amount of variation that is expected in the subgroup proportions.
Red points indicate subgroups that fail at least one of the tests for special causes and are not in control. If the same point fails multiple tests, then the point is labeled with the lowest test number to avoid cluttering the graph. If the chart shows out-of-control points, investigate those points.
Out-of-control points can influence the estimates of process parameters and prevent control limits from truly representing your process. If out-of-control points are due to special causes, then consider omitting these points from the calculations. For more information, go to Specify subgroups to estimate parameters for P Chart.
In these results, the average proportion of defectives is approximately 0.066. The process does not appear to be in control because the last two subgroups each failed at least one test for special causes. When you hold the pointer over a red point, you can get more information about the subgroup. To determine which tests each point fails, review the output.
Step 2: Identify which points failed each test
Investigate any subgroups that fail the tests for special causes. By default, Minitab conducts only Test 1, which detects points that fall outside of the control limits. However, if you conduct additional tests, then points can fail multiple tests. The output shows exactly which points failed each test, as shown here.
These results show that subgroup 52 failed both Test 1 and Test 2. Subgroup 53 failed Test 2.
Test Results for P Chart of Defective Units
| TEST 1. One point more than 3.00 standard deviations from center line. |
|---|
| Test Failed at points: 52 |
| TEST 2. 9 points in a row on same side of center line. |
| Test Failed at points: 52, 53 |
Note
When you use several tests at the same time, the sensitivity of the chart increases. However, the false alarm rate also increases, which can make you react to the test results unnecessarily.
For more information on each of the tests and when to use them, go to Using tests for special causes in control charts.
