In This Topic
Shelf life for a model with a fixed batch factor and only a lower specification limit
The model with time, batch, and the time*batch interaction
When the batch effect and the batch*time interaction are in the model, the fit for the ith batch at time xij uses the model that follows:
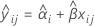
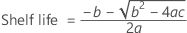
To find the shelf life, set the equation that follows equal to the lower specification limit and solve for time (x).
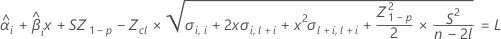
where

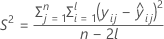
I = the total number of batch levels
n = the total number of response values
X = the design matrix for the model
To calculate a meaningful shelf life, Minitab evaluates three conditions. First, Minitab determines whether the mean response is statistically greater than the lower specification limit at time = 0.
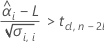
Second, Minitab determines whether the mean response declines at a statistically significant rate over time.

Third, Minitab determines whether the square root portion of the quadratic equation has a real number solution.
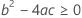
where
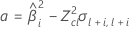
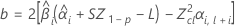
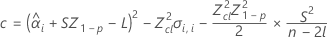
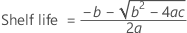
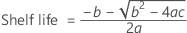
If all three conditions are true then Minitab calculates the shelf life. To calculate the shelf life, use the quadratic equation.
The model with time and batch
When the batch*time interaction is not in the model, the slopes are the same for every batch. The fit for the ith batch at time xij uses the model that follows:
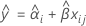
To find the shelf life, set the equation that follows equal to the lower specification limit and solve for time (x).
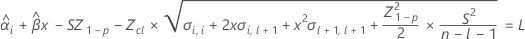
where

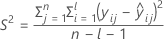
I = the total number of batch levels
n = the total number of response values
X = the design matrix for the model
To calculate a meaningful shelf life, Minitab evaluates three conditions. First, Minitab determines whether the mean response is statistically greater than the lower specification limit at time = 0.
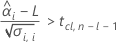
Second, Minitab determines whether the mean response declines at a statistically significant rate over time.
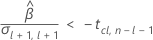
Third, Minitab determines whether the square root portion of the quadratic equation has a real number solution.
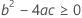
where
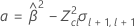

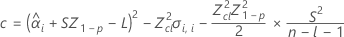
If all three conditions are true then Minitab calculates the shelf life. To calculate the shelf life, use the quadratic equation.
The model with time
When only time is in the model, the slopes and intercepts are the same for every batch. The fit at time xij uses the model that follows:
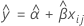
To find the shelf life, set the equation that follows equal to the lower specification limit and solve for time (x).
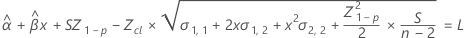
where
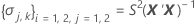
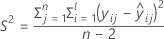
I = the total number of batch levels
n = the total number of response values
X = the design matrix for the model
To calculate a meaningful shelf life, Minitab evaluates three conditions. First, Minitab determines whether the mean response is greater than the lower specification limit at time = 0.
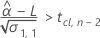
Second, Minitab determines whether the mean response declines over time.
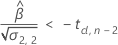
Third, Minitab determines whether the square root portion of the quadratic equation has a real number solution.
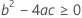
where


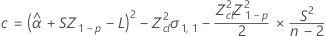
If all three conditions are true then Minitab calculates the shelf life. To calculate the shelf life, use the quadratic equation.
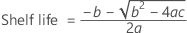
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
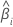 | the slope for the ith batch |
| Z | the value of the inverse cumulative probability function from the standard normal distribution with the given probability |
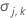 | the variance of the estimated parameter vector |
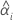 | the intercept for the ith batch |
| S2 | the mean square error |
| L | the lower specification limit |
| X | the design matrix |
| i | an index to show the batch that the shelf life estimate is for |
| l | the number of levels in the batch factor |
| n | the total number of response values |
Shelf life for a model with a fixed batch factor and only an upper specification limit
The model with time, batch, and the time*batch interaction
When the batch effect and the batch*time interaction are in the model, the fit for the ith batch at time xij uses the model that follows:
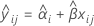
To find the shelf life, set the equation that follows equal to the upper specification limit and solve for time (x).
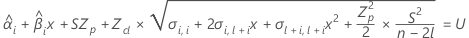
where
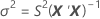
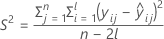
I = the total number of batch levels
n = the total number of response values
X = the design matrix for the model
To calculate a meaningful shelf life, Minitab evaluates three conditions. First, Minitab determines whether the mean response is statistically less than the upper specification limit at time = 0.
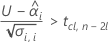
Second, Minitab determines whether the mean response increases at a statistically significant rate over time.

Third, Minitab determines whether the square root portion of the quadratic equation has a real number solution.
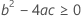
where
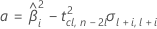

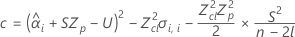
If all three conditions are true then Minitab calculates the shelf life. To calculate the shelf life, use the quadratic equation.
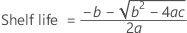
The model with time and batch
When the batch*time interaction is not in the model, the slopes are the same for every batch. The fit for the ith batch at time xij uses the model that follows:
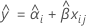
To find the shelf life, set the equation that follows equal to the upper specification limit and solve for time (x).
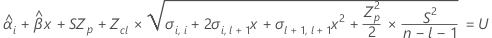
where

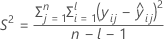
I = the total number of batch levels
n = the total number of response values
X = the design matrix for the model
To calculate a meaningful shelf life, Minitab evaluates three conditions. First, Minitab determines whether the mean response is statistically less than the upper specification limit at time = 0.
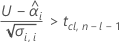
Second, Minitab determines whether the mean response increases at a statistically significant rate over time.
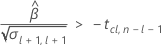
Third, Minitab determines whether the square root portion of the quadratic equation has a real number solution.
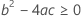
where

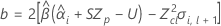
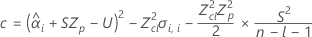
If all three conditions are true then Minitab calculates the shelf life. To calculate the shelf life, use the quadratic equation.
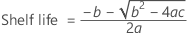
The model with time
When only time is in the model, the slopes and intercepts are the same for every batch. The fit at time xij uses the model that follows:
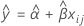
To find the shelf life, set the equation that follows equal to the upper specification limit and solve for time (x).

where
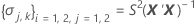
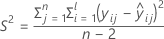
I = the total number of batch levels
n = the total number of response values
X = the design matrix for the model
To calculate a meaningful shelf life, Minitab evaluates three conditions. First, Minitab determines whether the mean response is less than the upper specification limit at time = 0.
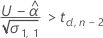
Second, Minitab determines whether the mean response increases over time.
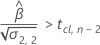
Third, Minitab determines whether the square root portion of the quadratic equation has a real number solution.
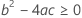
where
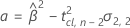

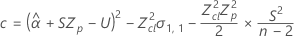
If all three conditions are true then Minitab calculates the shelf life. To calculate the shelf life, use the quadratic equation.
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
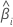 | the slope for the ith batch |
| Z | the value of the inverse cumulative probability function from the standard normal distribution with the given probability |
 | the variance of the estimated parameter vector |
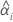 | the intercept for the ith batch |
| S2 | the mean square error |
| U | the upper specification limit |
| X | the design matrix |
| i | an index to show the batch that the shelf life estimate is for |
| l | the number of levels in the batch factor |
| n | the total number of response values |
Both limits
To simplify the calculation of the condition for how and when Minitab calculates the shelf life, consider which model you fit to the data.
The model with time, batch, and the time*batch interaction
Minitab evaluates two conditions to determine whether a meaningful estimate of the shelf life exists. First, Minitab determines whether the mean response is statistically within the specification limits.
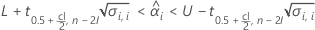
where

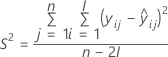
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| I | the total number of batch levels |
| n | the total number of response values |
| X | the design matrix for the model |
Second, Minitab determines whether the mean response changes at a statistically significant rate over time.
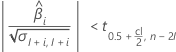
If a meaningful estimate exists, then Minitab determines whether the mean response increases or decreases over time. If the second conditions is false, then one of the conditions that follows is true.
If the response decreases with time, the Minitab calculates the shelf life relative to the lower specification limit. This formula gives the condition when the response decreases:
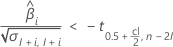
If the response increases with time, then Minitab calculates the shelf life relative to the upper specification limit. This formula gives the condition when the response increases:
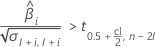
If the mean response decreases over time, then Minitab calculates the shelf life relative to the lower specification limit. Otherwise, Minitab calculates the shelf life relative to the upper specification limit.
For details on the calculation of the shelf life for each case, go to the corresponding section about the shelf life for that specification limit.
The model with time and batch
Minitab evaluates two conditions to determine whether a meaningful estimate of the shelf life exists. First, Minitab determines whether the mean response is statistically within the specification limits.
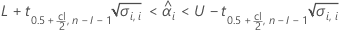
where

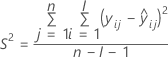
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| I | the total number of batch levels |
| n | the total number of response values |
| X | the design matrix for the model |
Second, Minitab determines whether the mean response changes at a statistically significant rate over time.
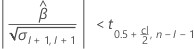
If a meaningful estimate exists, then Minitab determines whether to estimate the shelf life relative to the upper specification limit or the lower specification limit.
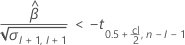
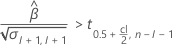
For details on the calculation of the shelf life for each case, go to the corresponding section about the shelf life for that specification limit.
The model with time
Minitab evaluates two conditions to determine whether a meaningful estimate of the shelf life exists. First, Minitab determines whether the mean response is statistically within the specification limits.
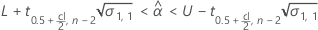
where

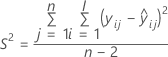
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| I | the total number of batch levels |
| n | the total number of response values |
| X | the design matrix for the model |
Second, Minitab determines whether the mean response changes at a statistically significant rate over time.
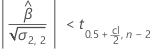
If a meaningful estimate exists, then Minitab determines whether to estimate the shelf life relative to the upper specification limit or the lower specification limit.
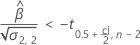
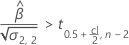
For details on the calculation of the shelf life for each case, go to the corresponding section about the shelf life for that specification limit.
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
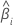 | The slope for the ith batch |
| I | the number of levels in the batch factor |
| n | the number of rows in the data |
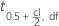 | the value of the inverse cumulative distribution at 0.5+cl/2 from the t distribution with df degrees of freedom |
