Select the method or formula of your choice.
In This Topic
Calculating power
Formula
One-sided power (H 1: λ > λ 0)
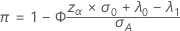
One-sided power (H 1: λ <λ 0)
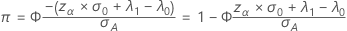
Two-sided power (H 1: λ ≠ λ 0)
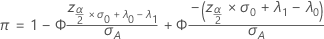
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Φ | the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the standard normal distribution |
| zα | Φ-1 (1 - α) where Φ-1 is the inverse CDF of the standard normal distribution |
| λ | the true value of the population rate |
| λ 0 | the hypothesized value of the population rate |
| λ 1 | the comparison rate |
| σ 0 | the standard deviation under null hypothesis equal to  |
| σ A | the standard deviation under alternative hypothesis equal to  |
Calculating sample size and comparison rate
If you provide values for power and sample size, Minitab calculates the value of the comparison rate. If you provide values for power and comparison rate, Minitab calculates the value of the sample size.
For these two cases, Minitab uses an iterative algorithm to find the optimal value. At each iteration, Minitab evaluates the power for a trial sample size or trial comparison rate, and stops when the power function equals a target power value.
Target power and actual power
When Minitab calculates sample size, it may find that no integer value of sample size yields your target power. In such cases, Minitab displays the target value for power alongside the actual power, which is a value corresponding to an integer sample size, and which is nearest to, yet greater than, the target value.
