Suppose you want to establish tolerances for each element in a brake assembly.
- Compare statistics from your own estimates of tolerances and those calculated using this procedure
- Limit the width of the gap by entering upper and lower gap specifications
The tolerancing procedure has two parts. The first part, described in this topic, uses Calculate Gap Pools. The output from this command determines how you do the second part of the procedure, which uses Allocate Gap Pools. For the second part of this example, go to Example of Allocate Gap Pools.
- Open the file Brake.MWX. (For a description of the worksheet, go to Data sets that are used in Six Sigma module help.)
- Choose .
- In Element names, enter Elements. In Means, enter Means.
- In Directional vectors, enter 'Dir Vectors'. In Standard deviations, enter 'St Dev'.
- In Long-term PPM, enter 3.397673. This is the default value and corresponds to having a long-term gap Z = 4.5.
- Under Gap Specifications, in Lower spec, type 0.001. In Upper spec, type 0.251.
- Click Options.
- In Complexity, enter Cmplx.
- In Lower spec, enter Lowers. In Upper spec, enter Uppers.
- Click OK in each dialog box.
Interpret the results
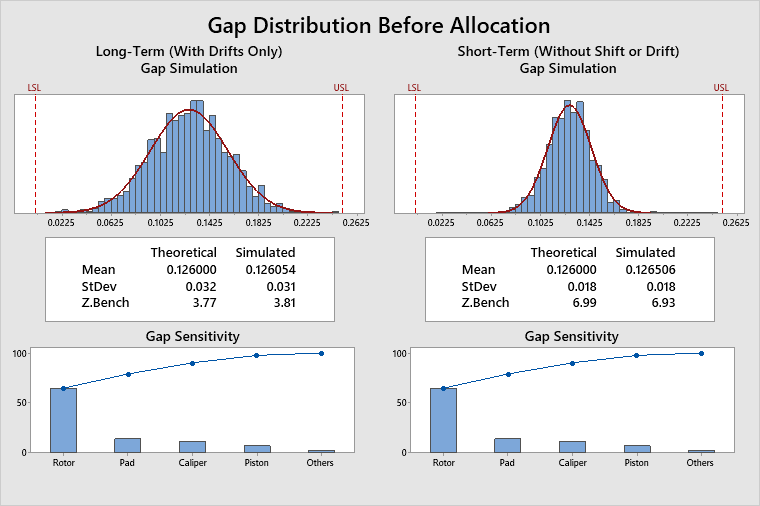
The long-term Gap Z.Bench is 3.77. However, a value of 4.5 is required to achieve the desired long-term PPM on the assembly gap.
The Gap Pool Statistics table shows the gap mean and variance pools. There is no mean pool to allocate, because, in this case, the short-term gap mean is equal to the midpoint between the gap specification limits. When this happens, the mean pool is always equal to 0. The variance pool is −0.0002839, which means that the long-term gap variance must be reduced by 0.0002839. To accomplish this, you must perform the second stage of the analysis, the allocation stage.