In This Topic
Plotted points
The plotted points on the I chart are the subgroup means.
The plotted points on the MR chart are the moving ranges of the subgroup means. The moving range is the absolute value of the difference between two or more consecutive points.
The plotted points on the R chart represent the subgroup ranges, and the plotted points on a S chart are the subgroup standard deviations.
Interpretation
If the process is in control, the points vary randomly around the center line, and the process exhibits only common-cause variation. Investigate points that fall outside the control limits or that exhibit nonrandom patterns for possible special-cause variation.
Center line
The center line on the I chart is an estimate of the process average. The center line on the MR chart is the average variation in the means of consecutive subgroups. The center line on the R or S chart is the average amount of variation within the subgroups.
Interpretation
Use the center line to observe how the process performs compared to the average. If the process is in control, then the points vary randomly around the center line.
CAUTION
Do not confuse the center line with the target value for your process. The target is your desired outcome. The center line is the actual outcome.
Control limits
CAUTION
Do not confuse control limits with specification limits. Specification limits represent customer requirements and indicate the amount of variation that you want to see in the process. Control limits represent the actual amount of variation that is in the sample data. A process can be in control, yet not be capable of meeting specifications.
Tests for special causes
The tests for special causes assess whether the plotted points are randomly distributed within the control limits.
Interpretation
Use the tests for special causes to determine which observations you may need to investigate and to identify specific patterns and trends in your data. Each of the tests for special causes detects a specific pattern or trend in your data, which reveals a different aspect of process instability. For example, Test 1 detects a single out-of-control point. Test 2 detects a possible shift in the process.
Eight tests are available with this control chart.
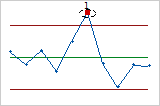
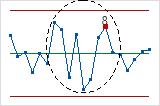
- Test 1: One point more than 3σ from center line
- Test 1 identifies subgroups that are unusual compared to other subgroups. Test 1 is universally recognized as necessary for detecting out-of-control situations. If small shifts in the process are of interest, you can use Test 2 to supplement Test 1 in order to create a control chart that has greater sensitivity.
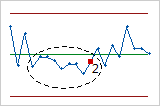
- Test 2: Nine points in a row on the same side of the center line
- Test 2 identifies shifts in the process centering or variation. If small shifts in the process are of interest, you can use Test 2 to supplement Test 1 in order to create a control chart that has greater sensitivity.
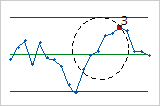
- Test 3: Six points in a row, all increasing or all decreasing
- Test 3 detects trends. This test looks for a long series of consecutive points that consistently increase in value or decrease in value.
- Test 4: Fourteen points in a row, alternating up and down
- Test 4 detects systematic variation. You want the pattern of variation in a process to be random, but a point that fails Test 4 might indicate that the pattern of variation is predictable.
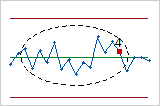
- Test 5: Two out of three points more than 2σ from the center line (same side)
- Test 5 detects small shifts in the process.
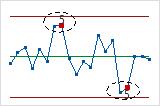
- Test 6: Four out of five points more than 1σ from center line (same side)
- Test 6 detects small shifts in the process.
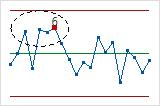
- Test 7: Fifteen points in a row within 1σ of center line (either side)
- Test 7 detects a pattern of variation that is sometimes mistaken as evidence of good control. This test detects control limits that are too wide. Control limits that are too wide are often caused by stratified data, which occur when a systematic source of variation is present within each subgroup.
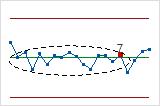
- Test 8: Eight points in a row more than 1σ from center line (either side)
- Test 8 detects a mixture pattern. In a mixture pattern, the points tend to fall away from the center line and instead fall near the control limits.
Standard deviations for I-MR-R/S Chart
The between-subgroup standard deviation is the variation that exists between subgroups. The within-subgroup standard deviation is the variation that exists within subgroups. The between/within standard deviation is an estimate of the total variation of the individual measurements.
Interpretation
Standard Deviations
| Between | 0.19619 |
|---|---|
| Within | 1.00753 |
| Between/Within | 1.02645 |
In these results, the between-subgroup standard deviation is 0.19619, the within-subgroup standard deviation is 1.00753, and the between/within (total standard deviation) standard deviation is 1.02645.
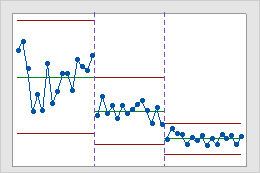
Stages
Use stages to create a historical control chart that shows how a process changes over specific periods of time. By default, Minitab recalculates the center line and control limits for each stage. For more information, go to Add stages to show how a process changed.
Interpretation
This historical control chart shows three stages of a process, which represent before, during, and after the implementation of a new procedure.