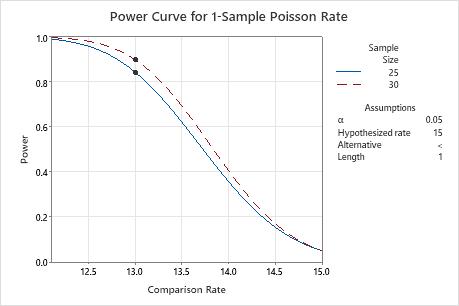
An automobile manufacturer wants to determine whether the number of defects on car doors before the cars are assembled is significantly less than 15. Before collecting the data for a 1-sample Poisson rate test, the manufacturer uses a power and sample size calculation. The manufacturer wants to determine what the power of the test will be when the sample size is either 25 or 30 and when the test can detect a comparison rate of at least 13.
- Choose .
- In Sample sizes, enter 25 30.
- In Comparison rates, enter 13.
- In Hypothesized rate, enter 15.
- Select Options.
- Under Alternative Hypothesis, select Less Than.
- Click OK in each dialog box.
Interpret the results
To detect a comparison rate of 13, the test will have a power of 0.843 when the sample size is 25, and a power of 0.898 when the sample size is 30. The manufacturer decides that 0.843 is enough power, and collects a sample size of 25.
Test for 1-Sample Poisson Rate
Testing rate = 15 (versus < 15)
α = 0.05
“Length” of observation = 1
Results
| Comparison Rate | Sample Size | Power |
|---|---|---|
| 13 | 25 | 0.842947 |
| 13 | 30 | 0.898200 |