Researchers for the NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) want to understand the relationship between the coefficient of thermal expansion for copper and the temperature in degrees Kelvin.
Previous research indicates that a nonlinear model with 7 parameters provides an adequate fit. The researchers use nonlinear regression to estimate the parameters in the model.
- Open the sample data, CopperExpansion.MWX.
- Choose .
- In Response, enter Expansion.
- In Edit directly, copy and paste, or type the following: (b1+b2*Kelvin+b3*Kelvin^2+b4*Kelvin^3)/(1+b5*Kelvin+b6*Kelvin^2+b7*Kelvin^3)
- Click Parameters.
- In Required starting values, enter these values:
Parameter Values b1 1 b2 -0.1 b3 0.005 b4 -1e-6 b5 -0.005 b6 0.001 b7 -1e-7 - Click OK in each dialog box.
Interpret the results
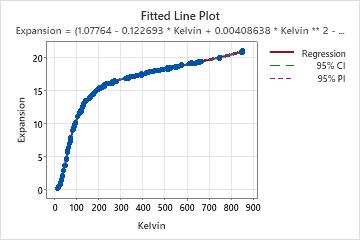
The fitted line plot shows that the fitted line follows the observed values, which visually indicates that the model fits the data. The p-value for the lack-of-fit test is 0.679, which provides no evidence that the model fits the data poorly.
The warning about highly correlated parameters indicates that at least one pair of parameters has a correlation greater than an absolute value of 0.99. However, because previous studies indicate that a nonlinear model with 7 parameters provides an adequate fit to the data, the researchers do not change the model.
Method
| Algorithm | Gauss-Newton |
|---|---|
| Max iterations | 200 |
| Tolerance | 0.00001 |
Starting Values for Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| b1 | 1 |
| b2 | -0.1 |
| b3 | 0.005 |
| b4 | -0.000001 |
| b5 | -0.005 |
| b6 | 0.001 |
| b7 | -0.0000001 |
Equation
3) / (1 - 0.00576099 * Kelvin + 0.000240537 * Kelvin ** 2 - 1.23144E-07 * Kelvin ** 3)
Parameter Estimates
| Parameter | Estimate | SE Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| b1 | 1.07764 | 0.170702 |
| b2 | -0.12269 | 0.012000 |
| b3 | 0.00409 | 0.000225 |
| b4 | -0.00000 | 0.000000 |
| b5 | -0.00576 | 0.000247 |
| b6 | 0.00024 | 0.000010 |
| b7 | -0.00000 | 0.000000 |
Lack of Fit
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error | 229 | 1.53244 | 0.0066919 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 228 | 1.52583 | 0.0066922 | 1.01 | 0.679 |
| Pure Error | 1 | 0.00661 | 0.0066125 |
Summary
| Iterations | 15 |
|---|---|
| Final SSE | 1.53244 |
| DFE | 229 |
| MSE | 0.0066919 |
| S | 0.0818039 |
