In This Topic
Histogram of residuals
The histogram of the residuals shows the distribution of the residuals for all observations.
Interpretation
| Pattern | What the pattern may indicate |
|---|---|
| A long tail in one direction | Skewness |
| A bar that is far away from the other bars | An outlier |
Because the appearance of a histogram depends on the number of intervals used to group the data, don't use a histogram to assess the normality of the residuals. Instead, use a normal probability plot.
A histogram is most effective when you have approximately 20 or more data points. If the sample is too small, then each bar on the histogram does not contain enough data points to reliably show skewness or outliers.
Normal probability plot of residuals
The normal probability plot of the residuals displays the residuals versus their expected values when the distribution is normal.
Interpretation
Use the normal probability plot of the residuals to verify the assumption that the residuals are normally distributed. The normal probability plot of the residuals should approximately follow a straight line.
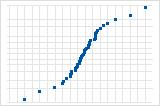
S-curve implies a distribution with long tails.
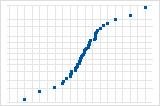
Inverted S-curve implies a distribution with short tails.
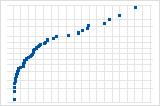
Downward curve implies a right-skewed distribution.
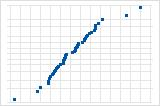
A few points lying away from the line implies a distribution with outliers.
If you see a nonnormal pattern, use the other residual plots to check for other problems with the model, such as missing terms or a time order effect. If the residuals do not follow a normal distribution, the confidence intervals and p-values can be inaccurate.
Residuals versus fits
The residuals versus fits graph plots the residuals on the y-axis and the fitted values on the x-axis.
Interpretation
Use the residuals versus fits plot to verify the assumption that the residuals are randomly distributed and have constant variance. Ideally, the points should fall randomly on both sides of 0, with no recognizable patterns in the points.
| Pattern | What the pattern may indicate |
|---|---|
| Fanning or uneven spreading of residuals across fitted values | Nonconstant variance |
| Curvilinear | A missing higher-order term |
| A point that is far away from zero | An outlier |
| A point that is far away from the other points in the x-direction | An influential point |
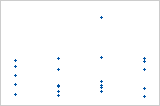
Plot with outlier
One of the points is much larger than all of the other points. Therefore, the point is an outlier. If there are too many outliers, the model may not be acceptable. You should try to identify the cause of any outlier. Correct any data entry or measurement errors. Consider removing data values that are associated with abnormal, one-time events (special causes). Then, repeat the analysis.
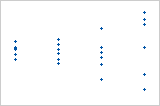
Plot with nonconstant variance
The variance of the residuals increases with the fitted values. Notice that, as the value of the fits increases, the scatter among the residuals widens. This pattern indicates that the variances of the residuals are unequal (nonconstant).
If you identify any patterns or outliers in your residual versus fits plot, consider the following solutions:
| Issue | Possible solution |
|---|---|
| Nonconstant variance | Consider using Fit Regression Model with a Box-Cox transformation or weights. |
| An outlier or influential point |
|
Residuals versus order
The residuals versus order plot displays the residuals in the order that the data were collected.
Interpretation
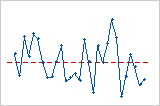
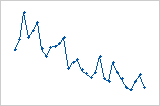
Trend
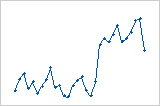
Shift
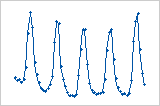
Cycle
Residuals versus the variables
The residual versus variables plot displays the residuals versus another variable. The variable could already be included in your model. Or, the variable may not be in the model, but you suspect it affects the response.
Interpretation
If you see a non-random pattern in the residuals, it indicates that the variable affects the response in a systematic way. Consider including this variable in an analysis.
Residual plots for a test data set
Interpretation
Because the training and test data sets are typically from the same population, you expect to see the same patterns in the residual plots for each data set. Different patterns in the residual plots could indicate a systematic difference between the observations in the training data set and the test data set.
Although the patterns are typically the same, the residual plots for the test data set can be slightly different from the plots for the training data set. For example, because the test data set is not in the model fitting process, the mean of the residuals can be non-zero.
