In This Topic
- Unbiasing constants for estimating long-term and short-term standard deviation
- Short-term standard deviations
- Long-term standard deviations
- Long-term process mean
- Long-term process standard deviation
- Short-term process mean
- Short-term process standard deviation
- Capability statistics
- Degrees of freedom
- Probabilities
- Z.bench statistics
Unbiasing constants for estimating long-term and short-term standard deviation
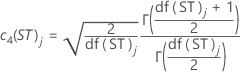
- Unbiasing constant for estimating long-term standard deviation
-
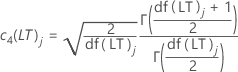
- Unbiasing constant for estimating short-term standard deviation
-
where:
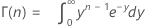
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| c4(LT)j | Unbiasing constant for long-term calculations at cumulative jth subgroup |
| c4(ST)j | Unbiasing constant for short-term calculations at cumulative jth subgroup |
| df(LT)j | Long-term degrees of freedom at jth subgroup |
| df(ST)j | Short-term degrees of freedom at jth subgroup |
Short-term standard deviations
- Short-term standard deviation with unbiasing constant (default)
-

- Short-term standard deviation without unbiasing constant
-
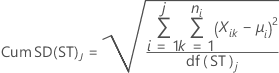
where:
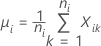
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Cum SD(ST)j | Cumulative short-term standard deviation up to the jth subgroup |
| c4(ST)j | Unbiasing constant for short-term calculations at cumulative jth subgroup |
| df(ST)j | Short-term degrees of freedom at jth subgroup |
Long-term standard deviations
- Long-term standard deviation without unbiasing constant (default)
-
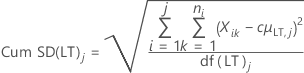
- Long-term standard deviation with unbiasing constant
-
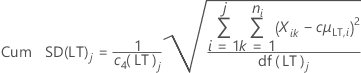
where:
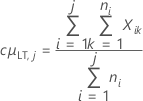
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Cum SD(LT)j | Cumulative long-term standard deviation up to the jth subgroup |
| c4(LT)j | Unbiasing constant for long-term calculations at cumulative jth subgroup |
| df(LT)j | Long-term degrees of freedom at jth subgroup |
Long-term process mean
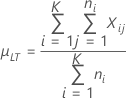
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
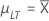
| µLT |
Long-term mean or process mean μLT = cμLT,K Note
|
Long-term process standard deviation
σLT = Cum SD(LT)K
Short-term process mean
- If target is given
- μST = T
- If both specs are given (no target)

- If one spec is given (no target)
- μST = μLT
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| µST | Short-term mean |
| T | Target |
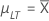
| µLT |
Long-term mean or process mean Note
|
Short-term process standard deviation
σST = Cum SD(ST)K
For more information, go to How Minitab chooses centering values for short-term statistics for Process Report.
Capability statistics
- CCpk
-

- Cp
-

- Cpk
-
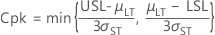
- CPL
-

- CPU
-

Note
Cp, Cpk, and CCpk represent the potential capability of the process. Therefore, these formulas use short-term variability.
- Pp
-

- Ppk
-
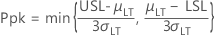
- PPL
-
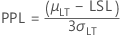
- PPU
-

Note
Pp and Ppk represent the actual process performance. Therefore, these formulas use long-term variability.
Degrees of freedom
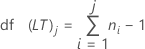
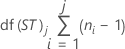
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| df(LT)j | Long-term degrees of freedom at jth subgroup |
| df(ST)j | Short-term degrees of freedom at jth subgroup |
Probabilities
- P.LSL(LT)j
-
Long-term probability of less than or equal to lower spec at jth subgroup
P.LSL(LT) j = 1 – Φ(Z.LSL(LT)j)
- P.LSL(ST) j
-
Short-term probability of less than or equal to lower spec at jth subgroup
P.LSL(ST) j = 1 – Φ(Z.LSL(ST)j)
- P.USL(LT) j
-
Long-term probability of greater than or equal to upper spec at jth subgroup
P.USL(LT) j = 1 – Φ(Z.USL(LT)j)
- P.USL(ST) j
-
Short-term probability of greater than or equal to upper spec at jth subgroup
P.USL(ST) j = 1 – Φ(Z.LSL(ST)j)
- P.Total(LT) j
-
Total (long-term) probability of out-of-spec at jth subgroup
P.Total(LT) j = P.USL(LT)j + P.LSL(LT)j
- P.Total(ST)j
-
Total (short-term) probability of out-of-spec at jthsubgroup
P.Total(ST)j = P.USL(ST)j + P.LSL(ST)j
Z.bench statistics
- Z.Bench(LT)j
-
Benchmark Z (long-term) at jth subgroup
Z.Bench(LT)j = Φ−1(P.Total(LT)j)
- Z.Bench(ST)j
-
Benchmark Z (short-term) at jth subgroup
Z.Bench(ST)j = Φ−1(P.Total(ST)j)
- Z.LSL(LT)j
-
Z-value (long-term) for lower spec at jth subgroup
Z.LSL(LT)j = (μLT – LSL) / Cum SD(LT)j
- Z.LSL(ST)j
-
Z-value (short-term) for lower spec at jth subgroup
Z.LSL(ST)j = (μST – LSL) / Cum SD(ST)j
- Z.USL(LT)j
-
Z-value (long-term) for upper spec at jth subgroup
Z.USL(LT)j = (USL – μLT) / Cum SD(LT)j
- Z.USL(ST)j
-
Z-value (short-term) for upper spec at jth subgroup
Z.USL(ST)j = (USL – μST) / Cum SD(ST)j
- Z.Shiftj
-
Shift factor at jth subgroup
Z.Shiftj = Z.Bench(ST)j – Z.Bench(LT)j