The calculations for the long-term statistics differ, depending on whether you specified shift or drift (variation expansion) factors for the elements and which gap specifications are given.
Shift and drift factors are used to accommodate unexpected errors or movement over time.
- Drift is a change in the variance over time, while the mean does not exhibit a systematic change.
- Shift is a systematic change i the mean over time. Typically, a shift of 1.5 sigma accommodates unexpected errors or movement over time.
For calculations for short-term statistics, go to Calculations for the gap distribution (short-term statistics) for Calculate Gap Pools.
Mean shift factor only
- One or no gap specification
-
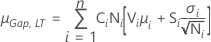
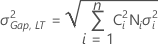
- Both gap specifications
-
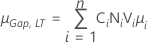
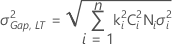
Note
ki = 1 + 8/15 |Si|
Variation expansion factor only
- One or no gap specification
-
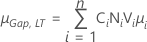

- Both gap specifications
-
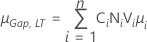
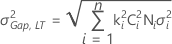
Note
ki = Di|
Both mean shift factor and variation expansion factor
- One or no gap specification
-
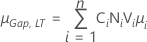
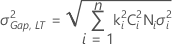
Note
ki = max{Di, 1 + 8/15 |Si|}
- Both gap specifications
-
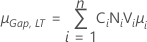
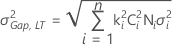
Note
ki = max{Di, 1 + 8/15 |Si|}
Neither mean shift factor nor variation expansion factor
- One or no gap specification
-
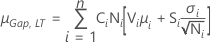
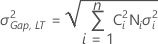
- Both gap specifications
-
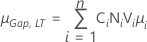
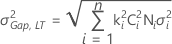
Note
ki = 1.8
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Ci | Diametrical correction of the ith element |
| Di | Drift factor for the ith element |
| Ni | Complexity of the ith element |
| Si | Shift factor for the ith element |
| σi | Standard deviation of the ith element |
| σadj,i | Adjusted standard deviation of the ith element |
| T | Gap targeted value (if not available, T = μGap,ST) |
| Ti | Nominal value of the ith element |
| μi | Mean of the ith element |
| μadj,i | Adjusted mean of the ith element |
| Vi | Directional vector of the ith element |
| wi | Allocation weight for the mean pool or the variance pool, ith element |
| Z.BenchGap,LT | Benchmark Z (long-term) of the gap |
| Z.BenchGap,ST | Benchmark Z (short-term) of the gap |
| Z.Benchi,LT | Benchmark Z (long-term) of the ith element |
| Z.Benchi,ST | Benchmark Z (short-term) of the ith element |
| ZP | Z-value, which gives desired PPM (right tail) for long-term gap distribution |
