Select the method or formula of your choice.
In This Topic
Probability plot
The probability plots include:
- Points, which are the estimated percentiles for corresponding probabilities of an ordered data set.
- Middle lines, which are the expected percentile from the distribution based on maximum likelihood parameter estimates. If the distribution is a good fit for the data, the points fall along the middle line.
Estimated probabilities
Minitab estimates the probability (P) that is used to calculate the plot points using the following methods.
- Median rank (Benard's method)
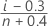
- Mean Rank (Herd-Johnson estimate)
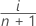
- Modified Kaplan-Meier (Hazen)
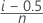
- Kaplan-Meier product limit estimate

Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| n | Number of observations |
| i | Rank of the ith ordered observation x(i), where x(1), x(2),...x(n) are the order statistics, or the data ordered from smallest to largest |
Plot points
The middle line of the probability plot is constructed using the x and y coordinate calculations in this table.
| Distribution | x coordinate | y coordinate |
|---|---|---|
| Smallest extreme value | x | ln(–ln(1 – p)) |
| Largest extreme value | x | ln(–ln p) |
| Weibull | ln(x) | ln(–ln(1 – p)) |
| Exponential | ln(x) | ln(–ln(1 – p)) |
| Lognormal | ln(x) | Φ–1norm |
| Logistic | x |
 |
| Loglogistic | ln(x) |
 |
| Gamma | x | Φ–1gamma |
Note
Because the plot points do not depend on any distribution, they are the same (before being transformed) for any probability plot. However, the fitted line differs depending on the parametric distribution chosen.
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| p | The estimated probability |
| Φ-1norm | Value returned for p by the inverse CDF for the standard normal distribution |
| Φ-1gamma | Value returned for p by the inverse CDF for the incomplete gamma distribution |
| ln(x) | The natural log of x |
