Maximum likelihood estimates
Maximum likelihood estimates of the parameters in the distribution are calculated by maximizing the likelihood function with respect to the parameters. For a given data set, the maximum likelihood estimates are the most likely values for the distribution parameters.
The Newton-Raphson algorithm is used to calculate maximum likelihood estimates of the distribution parameters. The Newton-Raphson algorithm is an iterative numerical method for calculating the maximum of a function. 1
Note
Minitab calculates the parameter estimates using the maximum likelihood method for all the distributions except the lognormal distribution. For the lognormal distribution, Minitab calculates unbiased parameter estimates.
Probability distributions
Lognormal distribution
 |
|
| CDF |
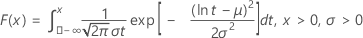 |
| Mean |
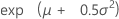 |
| Stdev |
 |
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| μ | Scale parameter |
| σ | Shape parameter |
Gamma distribution
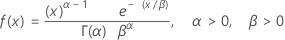 |
|
| CDF |
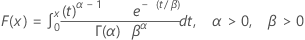 |
| Mean | αβ |
| Stdev | αβ2 |
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| α | Shape parameter |
| β | Scale parameter |
Exponential distribution
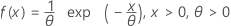 |
|
| CDF |
 |
| Mean | θ |
| Stdev | θ |
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| θ | Scale parameter |
Smallest extreme value distribution
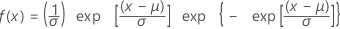 |
|
| CDF |
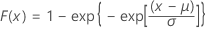 |
| Mean |
 |
| Stdev |
 |
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| μ | Location parameter |
| σ | Scale parameter |
| γ | Euler's constant (approximately equals 0.5772) |
Weibull distribution
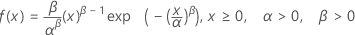 |
|
| CDF |
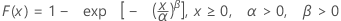 |
| Mean |
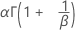 |
| Stdev |
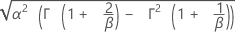 |
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| α | Scale parameter |
| β | Shape parameter |
Largest extreme value distribution
 |
|
| CDF |
 |
| Mean |
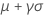 |
| Stdev |
 |
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| μ | Location parameter |
| σ | Scale parameter |
| γ | Euler's constant (approximately equals 0.5772) |
Logistic distribution
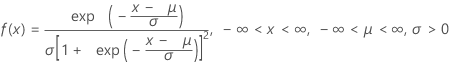 |
|
| CDF |
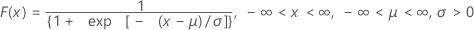 |
| Mean | μ |
| Stdev |
 |
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| μ | Location parameter |
| σ | Scale parameter |
Loglogistic distribution
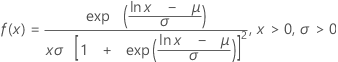 |
|
| CDF |
 |
| Mean |
 |
| Stdev |
 |
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| μ | Location parameter |
| σ | Scale parameter |
