Step 1: View the fit of the distribution
Use the probability plot to assess how closely your data follow each distribution.
If the distribution is a good fit for the data, the points should fall closely along the fitted distribution line. Departures from the straight line indicate that the fit is unacceptable.
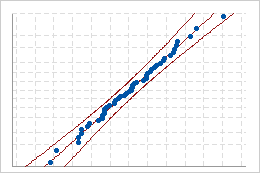
Good fit
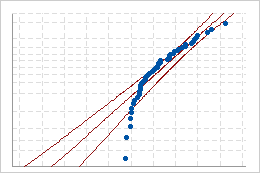
Poor fit
In addition to the probability plots, use the goodness-of-fit measures, such as the p-values, and your practical process knowledge, to evaluate the distribution fit.
Step 2: Assess the fit of the distribution
Use the p-value to assess the fit of the distribution.
- P ≤ α: The data do not follow the distribution (Reject H0)
- If the p-value is less than or equal to the significance level, you reject the null hypothesis and conclude that your data do not follow the distribution.
- P > α: Cannot conclude the data do not follow the distribution (Fail to reject H0)
- If the p-value is greater than the significance level, you fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not enough evidence to conclude that the data do not follow the distribution. You can assume that the data follow the distribution.
- Choose the distribution that is most commonly used in your industry or application.
- Choose the distribution that provides the most conservative results. For example, if you are performing capability analysis, you can perform the analysis using different distributions and then choose the distribution that produces the most conservative capability indices. For more information, go to Distribution percentiles for Individual Distribution Identification and click "Percents and percentiles".
- Choose the simplest distribution that fits your data well. For example, if a 2-parameter and a 3-parameter distribution both provide a good fit, you might choose the simpler 2-parameter distribution.
Important
Use caution when you interpret results from a very small or a very large sample. If you have a very small sample, a goodness-of-fit test may not have enough power to detect significant deviations from the distribution. If you have a very large sample, the test may be so powerful that it detects even small deviations from the distribution that have no practical significance. Use the probability plots in addition to the p-values to evaluate the distribution fit.
Goodness of Fit Test
| Distribution | AD | P | LRT P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 0.754 | 0.046 | |
| Box-Cox Transformation | 0.414 | 0.324 | |
| Lognormal | 0.650 | 0.085 | |
| 3-Parameter Lognormal | 0.341 | * | 0.017 |
| Exponential | 20.614 | <0.003 | |
| 2-Parameter Exponential | 1.684 | 0.014 | 0.000 |
| Weibull | 1.442 | <0.010 | |
| 3-Parameter Weibull | 0.230 | >0.500 | 0.000 |
| Smallest Extreme Value | 1.656 | <0.010 | |
| Largest Extreme Value | 0.394 | >0.250 | |
| Gamma | 0.702 | 0.071 | |
| 3-Parameter Gamma | 0.268 | * | 0.006 |
| Logistic | 0.726 | 0.034 | |
| Loglogistic | 0.659 | 0.050 | |
| 3-Parameter Loglogistic | 0.432 | * | 0.027 |
| Johnson Transformation | 0.124 | 0.986 |
Key Results: P
In these results, several distributions have a p-value that is greater than 0.05. The 3-parameter Weibull distribution (P > 0.500) and the largest extreme value distribution (P > 0.250) have the largest p-values, and appear to fit the sample data better than the other distributions. Also, the Box-Cox transformation (P = 0.353) and the Johnson transformation (P = 0.986) are effective in transforming the data to follow a normal distribution.
Note
For several distributions, Minitab also displays results for the distribution with an additional parameter. For example, for the lognormal distribution, Minitab displays results for both the 2-parameter and 3-parameter versions of the distribution. For distributions that have additional parameters, use the likelihood-ratio test p-value (LRT P) to determine whether adding another parameter significantly improves the fit of the distribution. An LRT p-value that is less than 0.05 suggests that the improvement in fit is significant. For more information, go to Goodness of fit for Individual Distribution Identification and click "LRT P".
