What is an average outgoing quality (AOQ) curve?
The average outgoing quality (AOQ) plot depicts the relationship between the quality of the incoming material and the quality of the outgoing material, assuming that rejected lots will be 100% inspected and that a rectifying inspection of defective items will be performed. In a rectifying inspection, defective items are either removed, reworked, or replaced.
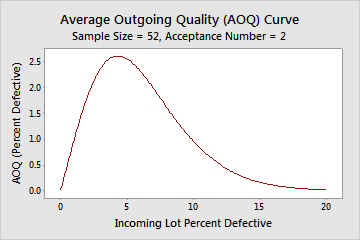
For example, you sample 52 pens from a shipment of 5000. If the actual % defective is 1.5%, the average outgoing quality is 1.42% defective.
In addition to the AOQ curve, you should also examine the OC curves and the ATI curves when rectifying inspection is required.
What is the average outgoing quality limit (AOQL)?
The average outgoing quality limit (AOQL) represents the maximum %defective in the outgoing product.
The average outgoing quality (AOQ) depends on the incoming quality, the probability that the lot will be accepted, and the sample and lot sizes. When incoming quality is very good, outgoing quality is very good. When incoming quality is very bad, the entire lot is rejected. Therefore, the outgoing quality is also very good because the lot will be rejected and the bad parts won't get through. When incoming quality is not very good or not very bad, the outgoing quality gets worse and the % defective in the outgoing level approaches a maximum known as the Average Outgoing Quality Limit (AOQL).
Use an AOQ curve to choose an appropriate sampling plan
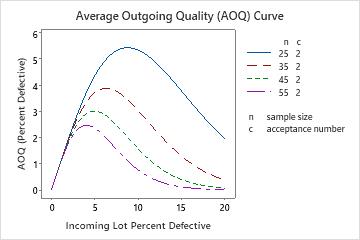
If the sample size is 35 (red line) and the %defective is 1.5%, the average outgoing quality is 1.37% defective.
