To use this function, choose .
Calculates the exponent to which 10 must be raised to equal a given number. For example, 102 = 100, so the log base 10 of 100 is 2. Log base 10 is defined only for positive numbers. When you multiply a number by 10, you increase its log by 1; when you divide a number by 10, you decrease its log by 1.
Syntax
LOGTEN(number)
In number, specify the value or column of values. Minitab computes the value x such that 10x = the number. If you enter 0 or a negative number, Minitab stores a missing value *.
Example
| Calculator expression | Result |
|---|---|
| LOGTEN(1000) | 4 |
Uses
- To make positively skewed data more "normal"
- To account for curvature in a linear model
- To stabilize variation within groups
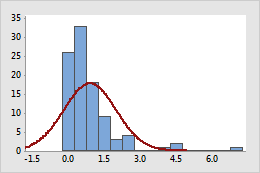
Original
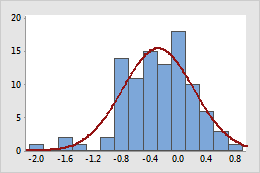
Log10 transform
Example of transforming data to make it appear more normal
In the original graph, the data are positively skewed as shown by the values far out on the right (upper) tail. The log10 transformation compresses the upper tail and stretches out the lower tail, making the transformed data appear more normal.
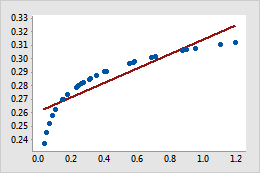
Original
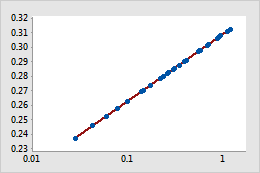
Log10 transform
Example of transforming data to account for curvature in a linear model
In the original scatterplot, the simple regression line does not accurately model the curvature in the data. After the X-scale is transformed using log10, the data values fall along the simple regression line.
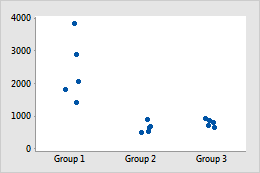
Original
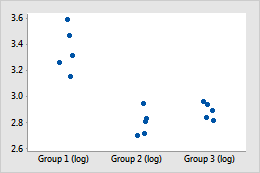
Log10 transform
Example of transforming data to stabilize variation within groups
In the original individual value plot, group 1 has larger values and thus appears to have greater within-group variability. After the data are transformed, the within-group variation appears similar.
