Wählen Sie die gewünschte Methode oder Formel aus.
In diesem Thema
Angepasste und prognostizierte Werte
Zum Berechnen der Prognose kehren Sie die Linkfunktion für das Modell um. Die Umkehrfunktionen finden Sie in der folgenden Tabelle.
| Linkfunktion | Formel für die Prognose |
|---|---|
| Logit | 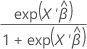 |
| Normit | 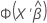 |
| Gompit |  |
Notation
| Begriff | Beschreibung |
|---|---|
| exp(·) | Exponentialfunktion |
| Φ(·) | kumulative Verteilungsfunktion der Normalverteilung |
| X' | transponierter Vektor der Punkte, für die Prognosen vorgenommen werden sollen |
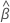 | Vektor der geschätzten Koeffizienten |
Standardfehler der angepassten Werte und Prognosen
Im Allgemeinen hat der Standardfehler der Anpassung die folgende Form:
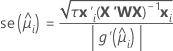
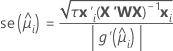
Die folgenden Formeln geben den Standardfehler der Passung für verschiedene Linkfunktionen an:
- Logit
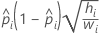
- Normit
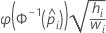
- Gompit

Beachten Sie die folgende Beziehung, die für die Formeln in der Tabelle gilt: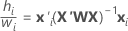
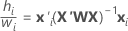
Hierbei ist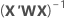 aus den Trainingsdaten nur, wenn ein Testdatensatz für die Validierung vorhanden ist.
aus den Trainingsdaten nur, wenn ein Testdatensatz für die Validierung vorhanden ist.
Notation
| Begriff | Beschreibung |
|---|---|
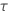 | 1, for the binomial and Poisson models |
| xi | the vector of a design point |
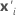 | the transpose of xi |
| X | the design matrix |
| W | the weight matrix |
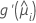 | the first derivative of the link function evaluated at 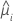 |
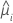 | the predicted mean response |
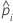 | the predicted probability for the design point in a binary logistic model |
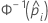 | the inverse cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution for the predicted probability in a binary logistic model |
 | the probability density function of the standard normal distribution |
Konfidenzgrenzen für Anpassungen und Prognosen
Für die Konfidenzgrenzen wird die Approximationsmethode nach Wald verwendet. Die Formel für ein beidseitiges 100(1 – α)%-Konfidenzintervall lautet:
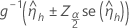
Notation
| Begriff | Beschreibung |
|---|---|
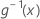 | Umkehrung der Linkfunktion, ausgewertet bei x |
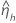 | 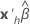 |
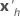 | transponierter Vektor der Prädiktoren |
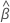 | Vektor der geschätzten Koeffizienten |
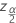 | Wert der inversen kumulativen Verteilungsfunktion der Normalverteilung, ausgewertet bei  |
| α | Signifikanzniveau |
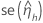 |  |
| X | Versuchsplanmatrix |
| W | Gewichtungsmatrix |
 | 1, für Binomialmodelle |
