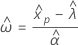Percentiles and standard errors of percentiles
Percentiles are estimates of the times at which a certain percent of the population has failed. By default, Minitab displays tables of percentiles for parametric distribution analysis for common percentiles.
The standard errors for the percentile estimates are the square root of the variances.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 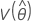 ,
, 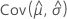 ,
, 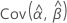 ,
, 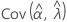 ,
, 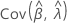 ,
, 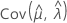 and
and 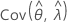 denote the variances and covariances of the MLEs of μ, σ, α, β, θ, and λ, which are taken from the appropriate element of the inverse of the Fisher information matrix.
denote the variances and covariances of the MLEs of μ, σ, α, β, θ, and λ, which are taken from the appropriate element of the inverse of the Fisher information matrix.
The formulas used for percentile and variance estimates for each distribution are as follows:
Smallest extreme value
- Percentile
-
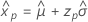
- Variance
-
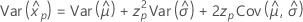
Weibull
- Percentile
-

- Variance
-
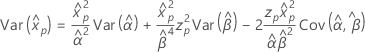
3-parameter Weibull
- Percentile
-

- Variance
-
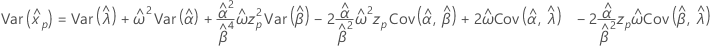
Exponential
- Percentile
-

- Variance
-

2-parameter exponential
- Percentile
-

- Variance
-
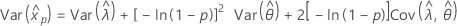
Normal
- Percentile
-
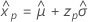
- Variance
-
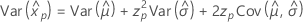
Lognormal
- Percentile
-

- Variance
-
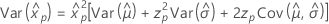
3-parameter lognormal
- Percentile
-

- Variance
-
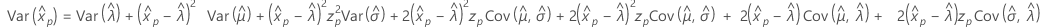
Logistic
- Percentile
-
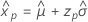
- Variance
-
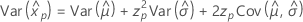
Loglogistic
- Percentile
-
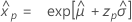
- Variance
-
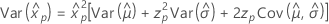
3-parameter loglogistic
- Percentile
-

- Variance
-

Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| zp |
the inverse cdf of the standard distribution evaluated at p (the pth percentile of the standard distribution) |
Confidence limits for percentiles
| Distribution | Confidence limits |
|---|---|
|
Smallest extreme value Normal Logistic |
  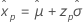 |
|
Weibull Exponential Lognormal Loglogistic |
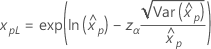 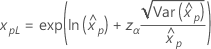 where |
|
3-parameter Weibull 2-parameter exponential 3-parameter lognormal 3-parameter loglogistic |
If λ < 0:   If λ 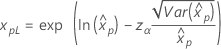 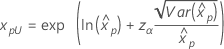 where |
For the calculations of the variance of the estimated xp, see the section "Percentiles and standard error of percentiles".
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| zα | the 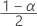 upper critical value for the standard normal distribution where 100α % is the confidence level. upper critical value for the standard normal distribution where 100α % is the confidence level. |