A healthcare consultant wants to compare the patient satisfaction ratings of two hospitals. The consultant performs a randomization test for 2-sample means to determine whether there is a difference in the patient ratings between the hospitals.
- Open the sample data, HospitalComparison.MWX.
- Choose .
- In Samples, enter Rating.
- In Sample IDs, enter Hospital.
- Click Options. Enter 1 in Base for random number generator.
Note
Using Base for random number generator ensures that your results match the example.
- Click OK in each dialog box.
Interpret the results
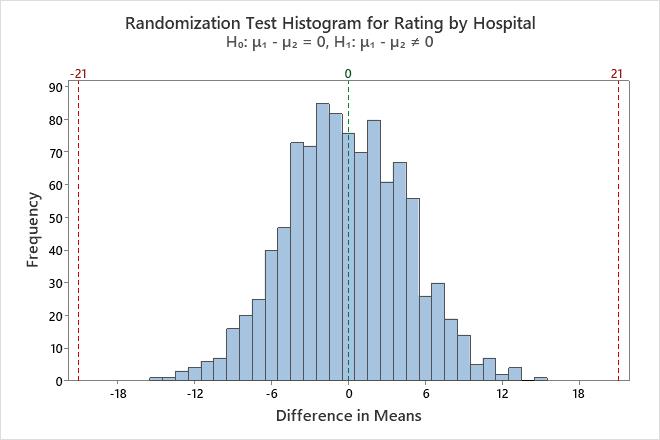
The null hypothesis states that the difference in the patient ratings between the hospitals is equal to 0. Because the p-value is less than 0.002, which is less than the significance level of 0.05, the consultant rejects the null hypothesis and concludes that the difference in patient ratings between the hospitals is not equal to 0. The histogram shows that the bootstrap distribution appears to be normal, so the consultant can trust the results.
The difference in observed means is 21, indicating that hospital A has higher patient satisfaction ratings than hospital B.
Method
| μ₁: population mean of Rating when Hospital = A |
|---|
| µ₂: population mean of Rating when Hospital = B |
| Difference: μ₁ - µ₂ |
Observed Samples
| Hospital | N | Mean | StDev | Variance | Minimum | Median | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 20 | 80.30 | 8.18 | 66.96 | 62.00 | 79.00 | 98.00 |
| B | 20 | 59.30 | 12.43 | 154.54 | 35.00 | 58.50 | 89.00 |
Difference in Observed Means
| Mean of A - Mean of B = 21.000 |
|---|
Randomization Test
| Null hypothesis | H₀: μ₁ - µ₂ = 0 |
|---|---|
| Alternative hypothesis | H₁: μ₁ - µ₂ ≠ 0 |
| Number of Resamples | Average | StDev | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | -0.185 | 4.728 | < 0.002 |
