In This Topic
Step 1: Check your data for problems
Your process should be stable and the original (or transformed) process data should follow a normal distribution. The control charts and probability distribution plot help you to evaluate whether these requirements are met.
Determine whether your process is stable
Control charts help you monitor the stability of your process by identifying out-of-control points and patterns and trends in your data.
Red points indicate subgroups that fail at least one of the tests for special causes and are not in control. Out-of-control points indicate that the process may not be stable and that the results of a capability analysis may not be reliable. You should identify the cause of out-of-control points and eliminate special-cause variation before you analyze process capability.
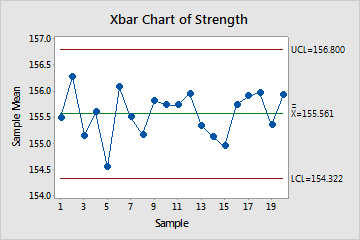
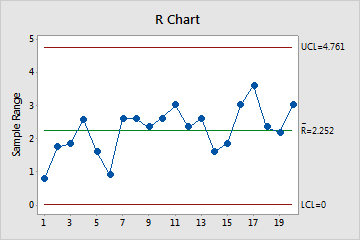
In these charts, the points vary randomly around the center line and are within the control limits for both charts. No trends or patterns are present. The process is stable across the 20 subgroups.
Note
The type of control chart that Minitab displays depends on the size of the subgroups in your data:
- If the subgroup size is 1, Minitab displays an I chart with an MR chart
- If the subgroup size is greater than 1, Minitab displays an Xbar chart with either an R chart (when the subgroup is from 2 to 8) or an S chart (when the subgroup size is 9 or more).
Assess the normality of your data
Use the normal probability plot to assess the requirement that your data follow a normal distribution.
If the normal distribution is a good fit for the data, the points form an approximately straight line and fall along the fitted line that is located between the confidence bounds. Departures from this straight line indicate departures from normality. If the p-value is greater than 0.05, you can assume that the data follow the normal distribution. You can evaluate the capability of your process using a normal distribution.
If the p-value is less than 0.05, your data are not normal and the capability analysis results may not be accurate. Use Individual Distribution Identification to determine whether you must transform the data or fit a nonnormal distribution to perform the capability analysis.
Note
If your data are nonnormal, you can use the Transform option included in this analysis to transform the data. To fit a nonnormal distribution to your data, use Nonnormal Capability Sixpack.
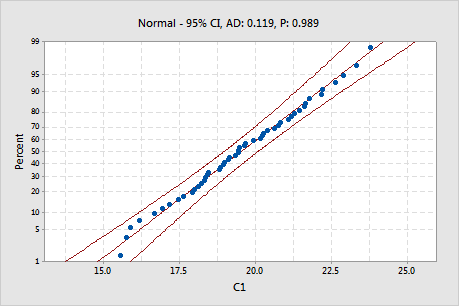
Key Result: P-value
In this plot, the points fall in an approximately straight line along the fitted (middle) line. The p-value is greater than 0.05, so there is not sufficient evidence that the data are not normally distributed. These data can be evaluated using normal capability analysis.
Step 2: Examine the observed performance of the process
Use the capability histogram to visually examine the sample observations in relation to the process requirements.
Examine the process spread
Visually examine the data in the histogram in relation to the lower and upper specification limits. Ideally, the spread of the data is narrower than the specification spread, and all the data are inside the specification limits. Data that are outside the specification limits represent nonconforming items.
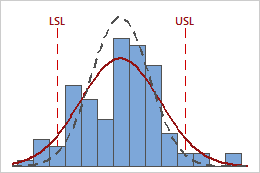
In this histogram, the process spread is larger than the specification spread, which suggests poor capability. Although most of the data are within the specification limits, there are nonconforming items below the lower specification limit (LSL) and above the upper specification limit (USL).
Note
To determine the actual number of nonconforming parts in your process, use the results for PPM.
Assess the center of the process
Evaluate whether the process is centered between the specification limits or at the target value, if you have one. The center of the data occurs at the peak of the distribution curve and is estimated by the sample mean.
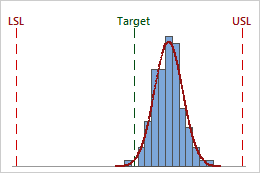
In this histogram, although the sample observations fall inside of the specification limits, the peak of the distribution curve is not centered on the target. Most of the data exceed the target value and are close to the upper specification limit..
Step 3: Evaluate the capability of the process
Use the main capability indices to evaluate how well your process meets requirements.
Assess potential capability
Use Cpk to evaluate the potential capability of your process based on both the process location and the process spread. Potential capability indicates the capability that could be achieved if process shifts and drifts were eliminated.
Generally, higher Cpk values indicate a more capable process. Lower Cpk values indicate that your process may need improvement.
-
Compare Cpk with a benchmark that represents the minimum value that is acceptable for your process. Many industries use a benchmark value of 1.33. If Cpk is lower than your benchmark, consider ways to improve your process, such as reducing its variation or shifting its location.
-
Compare Cp and Cpk. If Cp and Cpk are approximately equal, then the process is centered between the specification limits. If Cp and Cpk differ, then the process is not centered.
Key Result: Cpk
For the process data shown below, Cpk is 1.09. Because Cpk less than 1.33, the potential capability of the process does not meet customer requirements. The process is running too close to the lower specification limit. The process is not centered, so Cpk does not equal Cp (2.76).
Assess overall capability
Use Ppk to evaluate the overall capability of your process based on both the process location and the process spread. Overall capability indicates the actual performance of your process that your customer experiences over time.
Generally, higher Ppk values indicate a more capable process. Lower Ppk values indicate that your process may need improvement.
-
Compare Ppk to a benchmark value that represents the minimum value that is acceptable for your process. Many industries use a benchmark value of 1.33. If Ppk is lower than your benchmark, consider ways to improve your process.
-
Compare Pp and Ppk. If Pp and Ppk are approximately equal, then the process is centered between the specification limits. If Pp and Ppk differ, then the process is not centered.
-
Compare Ppk and Cpk. When a process is in statistical control, Ppk and Cpk are approximately equal. The difference between Ppk and Cpk represents the improvement in process capability that you could expect if shifts and drifts in the process were eliminated.

Key Result: Ppk
For these process data, Ppk = 0.52. Because Ppk is less than 1.33, the overall capability of the process does not meet customer requirements. The process is centered, so Ppk ≈ Pp (0.53). However, Ppk < Cpk (0.72), which indicates that the overall capability could be improved if the variation between subgroups were reduced.
Important
The Cpk and Ppk indices measure the capability of the process in relation only to the specification limit that is closest to the process mean. Therefore, these indices represent only one side of the process curve, and do not measure how the process performs on the other side of the process curve. If your process has nonconforming items that fall outside both specification limits, use additional capability measures to more fully assess process performance.
