In This Topic
Difference (D)
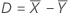
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| D | Difference |
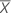 | Test mean |
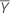 | Reference mean |
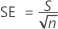
SE of the difference
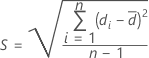
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| SE | Standard error of the difference |
| S | Standard deviation of the differences |
| n | Number of pairs of observations |
| di | Pairwise differences (X i - Yi), i = 1, ..., n |
 | Average of the pairwise differences |
Equivalence limits
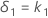
Let k1 be the value that you specify for the lower limit and k2 be the value that you specify for the upper limit. By default, the lower equivalence limit, δ1, is given by:
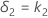
and the upper equivalence limit, δ2, is given by:
Degrees of freedom (DF)

Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| v | Degrees of freedom |
| n | Number of pairs of observations |
Confidence interval
100(1-α)% CI
By default, Minitab uses the following formula to calculate the 100(1 – α)% confidence interval (CI) for equivalence:
CI = [min(C, Dl), max(C, Du)]
where:

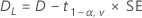
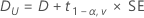
100(1-2α)% CI
If you select the option to use the 100(1 – 2α)% CI, then the CI is given by the following formula:
CI = [Dl, Du]
One-sided intervals
For a hypotheses of Test mean > reference mean or Test mean - reference mean > lower limit, the 100(1 – α)% lower bound is equal to DL.
For a hypothesis of Test mean < reference mean or Test mean - reference mean < upper limit, the 100(1 – α)% upper bound is equal to DU.Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| D | Difference between the test mean and the reference mean |
| SE | Standard error |
| δ1 | Lower equivalence limit |
| δ2 | Upper equivalence limit |
| v | Degrees of freedom |
| α | The significance level for the test (alpha) |
| t1-α, v | Upper 1 – α critical value for a t-distribution with v degrees of freedom |
T-values
 , and let t2 be the t-value for the hypothesis,
, and let t2 be the t-value for the hypothesis,  , where
, where  is the difference between the mean of the test population and the mean of the reference population. By default, the t-values are calculated as follows:
is the difference between the mean of the test population and the mean of the reference population. By default, the t-values are calculated as follows:


For a hypothesis of Test mean > reference mean, δ1 = 0.
For a hypothesis of Test mean < reference mean, δ 2 = 0.
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| D | Difference between the sample test mean and the sample reference mean |
| SE | Standard error of the difference |
| δ1 | Lower equivalence limit |
| δ2 | Upper equivalence limit |
P-values
| H0 | P-Value |
|---|---|
 |
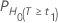 |
 |
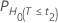 |
Notation
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
 | Unknown difference between the mean of the test population and the mean of the reference population |
| δ1 | Lower equivalence limit |
| δ2 | Upper equivalence limit |
| v | Degrees of freedom |
| T | t-distribution with v degrees of freedom |
| t1 | t-value for the hypothesis  |
| t2 | t-value for the hypothesis  |
Note
For information on how the t-values are calculated, see the section on t-values.
