Note
In the web app: After you run a simulation in the web app, select Parameter Optimization above the simulation results.
What is a parameter optimization?
Parameter optimization is used to identify optimal settings for the inputs that you can control. Workspace searches a range of values for each input to find settings that meet the defined objective and lead to better performance of the system. After a simulation analysis, you can perform a parameter optimization or a sensitivity analysis. However, for engineering applications, perform the parameter optimization prior to a sensitivity analysis because changing the system settings is often easier than changing the variability of the inputs. For example, adjusting the temperature setting is easier than reducing the variability of the temperature.
Perform a parameter optimization
When you perform a parameter optimization, Workspace searches for alternative input settings that optimize an output based on the objective and the search range you define.
- Choose .
- Choose the goal and the metric that you would like to affect for one of the outputs in your model.
-
To define the search range, enter the low and high settings of the
parameter values for the inputs that you can control. For inputs that you
cannot control, check
Noise.
Workspace
reruns the simulation and searches within these ranges to find settings that
improve the results based on your objective.
Tip
Consider using search ranges that are as wide as possible to broaden the search area and increase your chances of meeting your objective. Do not exceed levels that are unfeasible or unsafe for your system. You can repeat the parameter optimization and see how changing the search range affects the estimates of performance.
- Select Optimize Parameters.
Examine the results
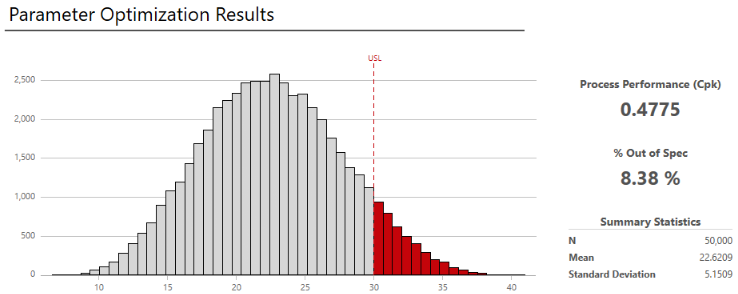
-
View the results in the workspace.
You can switch between the model view and the results view of
the simulation.
Note
Each time you repeat the simulation, the results will vary because the simulation is based on randomly selected values for the inputs.
- Under Assumptions, compare the new settings to the previous settings and confirm that the new settings are feasible for your application.
-
Evaluate the results, and perform any of the following tasks.
- To view capability, summary statistics, and percentiles, select More Results.
- If next steps are
available, hold the mouse pointer on
 to view more information.
to view more information.
- Perform another parameter optimization with wider ranges.
- Continue to optimize parameters until you are satisfied with the results. Next, you can perform a sensitivity analysis to examine the effects of changes to the input variation. For more information, go to Perform a sensitivity analysis.
Edit the model
Note
In the web app: Above the simulation results, select Edit Model to overwrite existing values in the model or select Duplicate to preserve the current settings and work in a copy of the model.
-
Choose one of the following options.
- To change the model, choose . By default, Workspace overwrites the existing values in the current model.
- To preserve the current settings and work in a copy, choose .
- Choose .
